Four Incredibly Significant Communicators/operators within our amazing body functioning simultaneously……
1.The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve and a primary component of the parasympathetic nervous system, controlling many involuntary functions, including heart rate, digestion, respiration, and mood. It also plays a crucial role in the gut-brain axis, facilitating communication between the brain and digestive tract. By stimulating the vagus nerve, one can support various aspects of physical and mental health, from reducing inflammation to improving mood.
2.Heart-Brain Communication that communication between the heart and brain actually is a dynamic, ongoing, two-way dialogue, with each organ continuously influencing the other’s function. Research has shown that the heart communicates to the brain in four major ways: neurologically (through the transmission of nerve impulses), biochemically (via hormones and neurotransmitters), biophysically (through pressure waves) and energetically (through electromagnetic field interactions). Communication along all these conduits significantly affects the brain’s activity. Moreover, research shows that messages the heart sends to the brain also can affect performance.
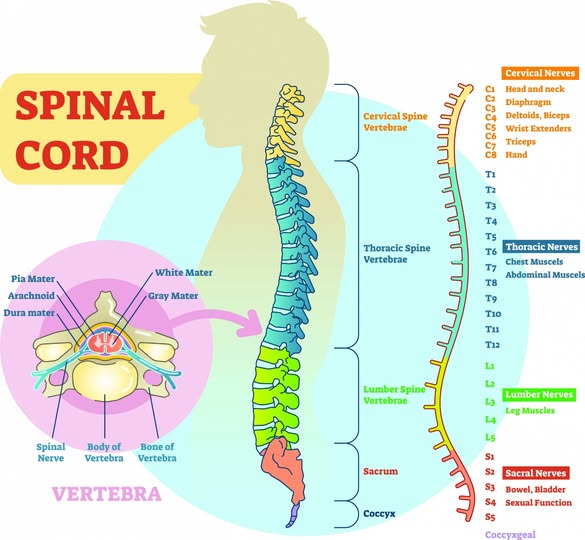
3.Spinal nerves are 31 pairs of mixed nerves that connect the spinal cord to the body, acting as a communication pathway between the central nervous system and the periphery. These nerves transmit sensory information from the body to the spinal cord and brain, and carry motor commands from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and other effector organs. They are also involved in autonomic functions through sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers.
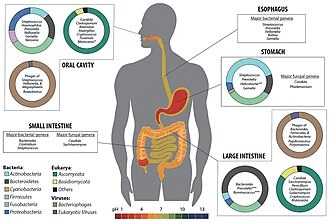
4.What is the gut microbiome?A biome is a distinct ecosystem characterized by its environment and its inhabitants. Your gut — inside your intestines — is in fact a miniature biome, populated by trillions of microscopic organisms. These microorganisms include over a thousand species of bacteria, as well as viruses, fungi and parasites.Gut microbes can affect your nervous system through the gut-brain axis — the network of nerves, neurons and neurotransmitters that runs through your GI tract. Certain bacteria actually produce or stimulate the production of neurotransmitters (like serotonin) that send chemical signals to your brain.Bacterial products may also affect your nervous system. Short-chain fatty acids appear to have positive effects, while bacterial toxins might damage nerves. Researchers continue to investigate how your gut microbiome might be involved in various neurological, behavioral, nerve pain and mood disorders.they contribute to human health and wellness in many ways.